As outside industries fuse with the cannabis market, we will begin to see innovations that will flesh out our understanding of cannabinoids and how they interact with the human body. I had the opportunity to sit down with chemist Dr. Mark Scialdone and Chris Barone, founder and lead chemist at The Clear™ to discuss the introduction of semi-synthetic cannabis compounds to the market. We focused on hydrogenated cannabinoids; cannabis with a slight twist that could change everything about why and how we consume cannabis.
Hydrogenation is simply treating a compound with hydrogen, which causes a chemical reaction between hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium, or platinum. This is done in order to reduce or saturate organic compounds, imbuing them with properties the original compounds did not have. These cannabinoid analogues (or semi-synthetic compounds) have a number of applications in manufacturing and medicine.
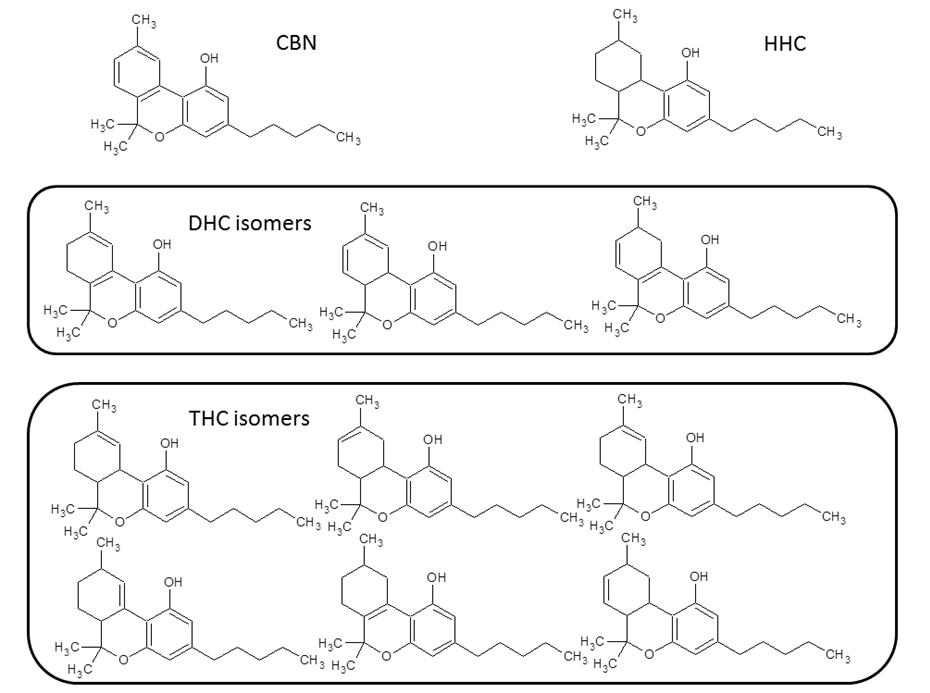
Hydrogenation is a minor modification to the natural framework of the compounds the cannabis plant produces biologically. Barone describes the process as, “adding hydrogens across the double bonds, thus changing the molecular weight, the molecules geometry, and also its effects on the body.”
Benefits of Hydrogenated Cannabinoids
A major benefit to hydrogenation is that it offers stability at the molecular level, assisting with both shelf life, and resistance to heat. Scialdone explained, “hydrogenation is a chemical transformation on unsaturated compounds to improve their stability and resistance to thermo-oxidative breakdown,” – which occurs when these compounds are in the presence of air. This is the reason you cannot leave cooking oils on the counter exposed to sunlight, as eventually this reaction will cause them to go rancid. Hydrogenation improves the oxidative stability by removing the unsaturation.
Based on a study referenced in Scialdone’s patents (US10071127B2 & US9694040B2), the effects of cannabinoids and hydrogenated cannabinoids were examined, in reference to tumor growth in mice. In these cases, the hydrogenated cannabinoids showed significant improvement in the reduction of tumor sizes; with Hexahydrocannabinolic Acid (HHCA) at a 39.70% reduction, and HCBDA at 55.83% reduction (compared to the non-hydrogenated compounds THCA at 37.67% and CBDA at 47.02%) (source). It’s possible that hexahydrocannabinoid (HHC), being more stable than tetrahydrocannabinoid (THC), and less prone to dehydrogenation (converting to DHC and CBN), may have an impact on resistance towards oxidative metabolic breakdown in the liver, though there is no critical examination at this time. It has been observed in metabolic studies that hydrogenated compounds are resistant to this kind of breakdown, suggesting that hydrogenated cannabinoids may exhibit this trait as well.